Iron.io Frequently Asked Questions
This a compilation of helpful answers to frequently asked questions. If you don't see your question on here, fear not! Just send us an email to support@iron.io and we'll get back you shortly. The Iron Team also encourages you to contribute to our documentation.Iron Heads Up Display
IronMQ
- What is IronMQ?
- What can I do with IronMQ?
- How do I get started with IronMQ?
- What resources are available on IronMQ?
- What are the benefits of IronMQ vs self-managed message queues?
- What are the benefits of IronMQ vs RabbitMQ?
- What are the benefits of IronMQ vs SQS?
- What happens to messages if no clients pull them off after put?
- Why are GETs and DELETEs separate actions?
- What is a push queue?
- What is the difference between unicast and multicast?
- Is the retry limit on unicast based on individual push attempt?
- Can a queue be a push queue and a pull queue at the same time?
- What security measures are used within IronMQ?
IronWorker
- What is IronWorker?
- What client libraries are available for IronWorker?
- What are the advantages of IronWorker vs Heroku Workers, Celery, or Resque?
- I'm getting this error "zip/zip (LoadError)"
- How do I access my worker's logs and what is printed in them?
IronCache
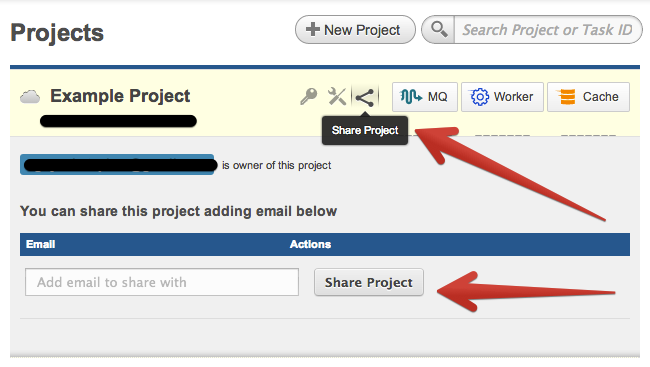
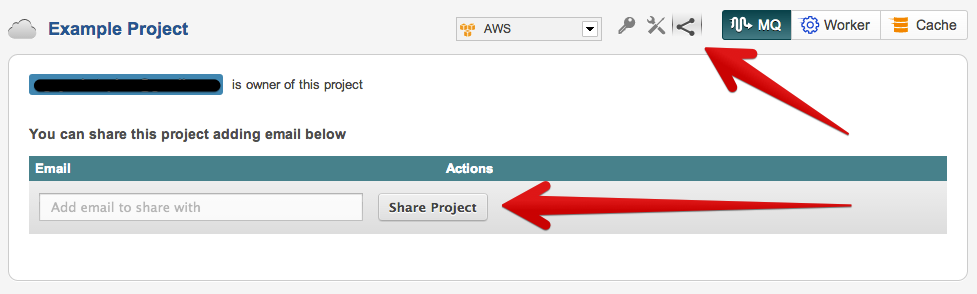
How do I share my Project/Account?
Sharing your Project by simply clicking on the share icon in our heads up display. If the user has an account they will immediately see your project otherwise a invite will be sent our asking them to join yours.
What is IronMQ?
IronMQ is an elastic message queue created specifically with the cloud in mind. It’s easy to use, runs on industrial-strength cloud infrastructure, and offers developers ready-to-use messaging with highly reliable delivery options and cloud-optimized performance.
What can I do with IronMQ?
A messaging layer is key to creating reliable and scalable distributed systems. It lets you orchestrate and manage the volume of messages and events that flow within your application and between other applications, sites, and services. IronMQ is a cloud-based solution that eliminates any setup or maintenance and provides work dispatch, load buffering, synchronicity, database offloading, and many other core needs for scalable cloud applications.
How do I get started with IronMQ?
Users can get up and running in a few minutes. Just sign up and get an auth token, and then you can send and receive messages on one or more queues. It’s that simple. Iron offers a free full-feature 14 day trial with no credit card required and so it’s easy to build in message queuing right from the start.
What resources are available on IronMQ?
See our developer section for information on how IronMQ works, API reference guide and other technical details. There are also a growing list of client libraries and framework integrations. These cover most common languages as well as frameworks such as Celery, YII, Laravel, DelayedJob and others.
What are the benefits of IronMQ vs self-managed message queues?
Cloud services provide many advantages over standing up software on self-managed servers. Primary ones include reduced complexity, greater speed to market, and increased reliability and scalability. It’s reasonably easy to stand up an open-source message queuing solution on a single virtual server but it’s exceedingly difficult to make a queuing system highly scalable and reliable. It takes multiple instances across zones or regions and redundancy within every layer and component including load balancing and the persistence layer. Robust logging and introspection tools add additional complexity. Multiply this across multiple environments, applications, systems, and business units, and the task of operating self-managed queues becomes almost impossible.
What are the benefits of IronMQ vs RabbitMQ?
RabbitMQ is an open-source packaged based on the AMQP protocol. It’s a strong messaging standard that has a lot of backing and inertia behind it. Unfortunately, it’s built for a different time – one that is pre-cloud and behind the firewall. It requires a lot of work to scale and make redundant and is more complex than most developers need. IronMQ is based on HTTP, takes JSON packages, and uses OAuth for authentication – all protocols and standards that are well-known to cloud developers. AMQP is a separate application layer protocol that is different than the one developers are used to using on a daily basis. AMQP also uses a less common default socket as part of the transport layer. Whereas certain cloud application hosts don’t allow most socket connections from within their sandbox, they do allow HTTP requests. HTTP and HTTPS are always open on most enterprise firewalls, but special ports may not always be. Everyone can easily speak HTTP, but it takes special effort to speak AMQP. This greatly limits the environments into which AMQP can be deployed. For more information on the differences between IronMQ and RabbitMQ, please see the comparison matrix on the website.
What are the benefits of IronMQ vs SQS?
For more information on the differences between IronMQ and SQS, please see the comparison matrix on the website.
What happens to messages if no clients pull them off after putting them in the queue?
Messages will persist in the queue until a receiver takes them off.
Why are GETs and DELETEs separate actions?
Receiving a message (GET) and deleting a message (DELETE) are separate actions because it provides a reliable paradigm for processing messages. An explicit delete protects messages from being only partially processed. If the receiving process dies or encounters an error, the message will be automatically put back on the queue once the timeout is reached.
What is a push queue?
A push queue is a queue that automatically pushes messages to endpoints. These endpoints can be HTTP/REST endpoints, IronMQ endpoints (in the form of a webhook), or an IronWorker endpoint (also in the form of a webhook). After a succesful push, messages are automatically deleted from the message queue.
What is the difference between unicast and multicast?
Unicast is a routing pattern that will cycle through the endpoints pushing to one endpoint after another until a success push occurs. Multicast is a routing pattern that will push the messages to all the subscribers.
Is the retry limit on unicast based on individual push attempts or based on the number of cycles of pushes?
It is transient so events and the associated data only exists until it has been delivered to all connected clients. If there are no clients subscribed to the channel that the message has been triggered on then that event is instantly lost. At present, we do not persist messages beyond the timeout value (default or user-set).
Can a queue be a push queue and a pull queue at the same time?
No. Queues are either on or the other (messages don’t last long on a push queue). You can switch from a pull queue to a push queue and vice versa at any point. (For example, to turn a push queue into a pull queue,you would just send push_type : pull.) Messages on a push queue at the time of a change will remain on the queue. You can also make a pull queue a subscriber of a push queue – either statically or by adding/deleting subscribers dynamically. (Just add the webhook endpoint for the pull queue as a subscriber for the push queue.)
What security measures are used within IronMQ?
Iron.io services run on top of industrial-strength clouds such as AWS and Rackspace and so we inherit many of their security measures and certifications that these clouds offer regarding VM security, network security, and physical security. Strong authentication using OAuth is provided to ensure that Iron.io accounts, services, and projects are secured against unauthorized access. Only account owners and accounts that queues have been shared with can access the queues, workers, and caches they create. We use SSL to protect data in transit and provide a high levels of security for the data within the system. We have a number of customers using us for transactional data and believe we offer a secure, reliable solution for cloud messaging. We do, however, recommend that for especially sensitive data, clients do client-level encryption of data payloads so that it has added protection even when data is at rest. We’re happy to discuss these measures as well as custom plans that can address areas that include SLAs, architectural help and enhanced support, and custom data retention options.
What happens once the set number of api requests, compute hours, or data volume in a plan isreached?
It’s up to you. Service can continue seamlessly on a usage-based rates or you can set a hard stop at the plan amount. The default is unlimited usage. See each service for the usage-based rates.
What happens if you turn the default off and hit the plan amount?
If you turn the default off and hit the plan limit, then subsequent API requests will return errors. (Specifically, the services will return an HTTP status code of 403.)
Can you adjust the plan limits?
You can either increase or decrease your plans at will. You can also turn on unlimited usage and you'll be billed at usage-based rates for amounts over the plan.
Will you be notified as you reach or exceed the plan amounts?
Yes. You’ll be notified on a regular basis of your usage as well as if you get close and/or reach the plan amounts. Note that you can switch plans at any time.
Can I pay at usage-based rates?
If you’re a heavy user and have specific needs, please let us know and we’d be happy to work with you to customize a plan that fits your needs. Contact us for more details.
What is IronWorker?
An easy-to-use scalable task queue that gives cloud developers a simple way to offload front-end tasks, run scheduled jobs, and process tasks in the background and at scale.
What are the advantages of IronWorker vs Heroku Workers, Celery, or Resque?
Our workers give you a wide range of flexibility and scalability that other services can't match. We support a wide range of languages. Python, Ruby, PHP, .NET, Java, Clojure, Node.js, Go, and binary code! Have a up to the second reporting and analytics though our Heads Up Display (HUD). By not having to manage your own servers, queues, and schedulers, we allow you scale accordingly to your needs, only processing time is counted.See our Comparison Chart
What client libraries are available for IronWorker?
We current have 6 official client libraries in Ruby, PHP, Python, Java, Node.js, and Go, as well as a unofficial client library for .Net.
- Ruby: http://github.com/iron-io/iron_worker_ruby_ng
- PHP: http://github.com/iron-io/iron_worker_php
- Python: http://github.com/iron-io/iron_worker_python
- Java: http://github.com/iron-io/iron_worker_java
- Node: http://github.com/iron-io/iron_worker_node
- Go: http://github.com/iron-io/iron_go
- .NET(unofficial): http://github.com/odeits/IronTools"
How do I access my worker's logs and what is printed in them?
IronWorker tasks print everything that would go to stdout (Standard Output) so the logs will very greatly depending on the worker's code and payload.
To access your IronWorker logs, log into your account and click the IronWorker icon on the top right. From there, select the task you need the logs from. From this page, you can click the log icon
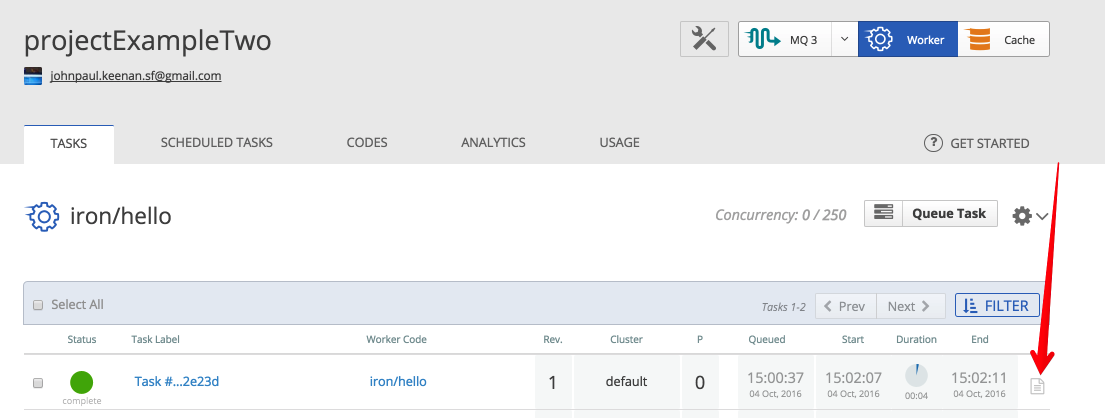
Or, click the task's label and access it from the task details.
What is IronCache?
IronCache is an elastic and durable key/value store that’s perfect for applications that need to share state, pass data, and coordinate activity between processes and devices. Reduce database load by making use of a high-performance middle tier for asynchronous processing and communication.
We keep an active presence on Twitter as @getiron, on Google+ as +Iron.io, and on Slack at get.iron.io/slack. Follow us, circle us, tweet us, or chat us up. We'd love to hear from you.